| |
Dry mixing – the uniform distribution of different components.
|
| |
 |
Fast and homogeneous
distribution with reproducible results.
Mixing of active ingredients,
additives and raw carrier materials.
|
Stable mixing
results.
No change in the mix due to transportation or storage.
|
Mixing of starting materials.
Powder.
|
| |
Mixing of intermediate products.
Granulates, etc.
|
| |
Process Principles
|
|
| |
|
| |
| |
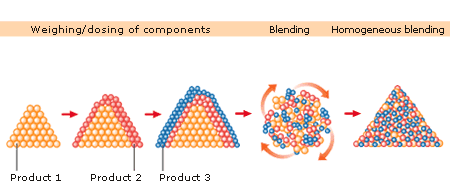
In solid processes, various individual products of different density and
concentration and in different amounts are often admixed to form a homogeneous
mixture. ( -> Container Blending)
In
the pharmaceutical area, very different quantities and proportions of active and
auxiliary ingredients (corn starch, lactose, PVP, etc.) are mixed
together.
Specific auxilliary materials such as lubricants or flavourings may
also be added.
Mixing may be necessary in different process sections. For
instance, compression aids, flow controlling media and external phases are added
following the granulation process and before compression.
|
| |
Requirements for the blending process
Defined mixing proportions
Dust free
Reproducible
Long shelf life
Homogeneous
|
|
Different blending optionsFor this process, Glatt offers drum and container blenders for container
sizes from 10l to 3000l/batch.
Blending processes can also be carried out before the process step Agglomeration/Granulation directly in the
vertical granulator or in the fluid bed system.
|
| |
|
|